Thermal paste is a heat-conducting compound applied to processors and other heat-generating components to improve heat dissipation. Some people wonder if it is also electrically conductive, as this could present a problem when used with certain types of hardware.
Metal-based thermal pastes are electrically conductive and can potentially cause damage to your computer if they come into contact with sensitive components. Carbon-based thermal pastes are not conductive and therefore pose no risk of short-circuiting.
In this article, we will explore whether thermal paste is electrically conductive and provide information on avoiding potential issues.
What is Thermal Paste and Why is it Used?
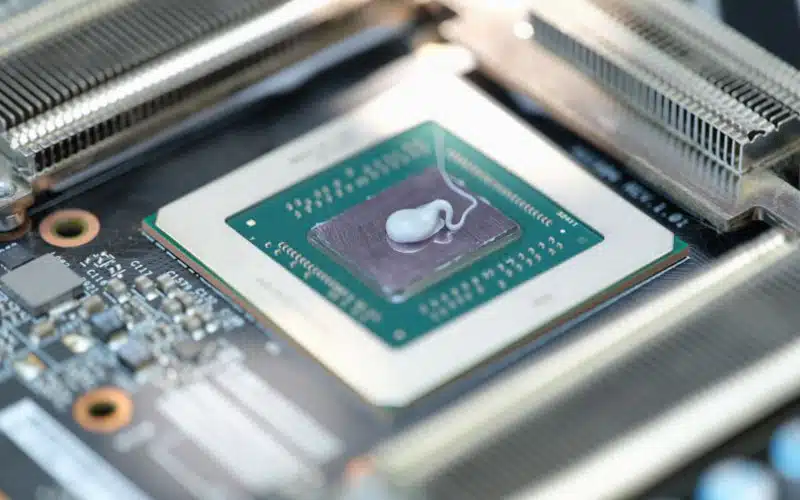
Thermal paste, also known as a thermal compound, thermal grease, or thermal interface material (TIM), is a substance used to improve the thermal conductivity between two surfaces in contact with each other. It is commonly used in electronics, such as computers and smartphones, to help dissipate heat away from components such as processors and graphics cards.
Thermal paste is typically applied between a heat sink and a processor or other heat-generating component. It helps to fill in any gaps or irregularities between the two surfaces, allowing for better heat transfer and improved cooling performance.
Without thermal paste, heat may not be able to dissipate effectively, which can lead to overheating and reduced performance of the component.
One question that often arises regarding thermal paste is whether or not it is electrically conductive. In other words, does it allow electricity to pass through it? The answer to this question is not straightforward, as it depends on the specific type of thermal paste.
Related: Thermal Paste on CPU Pins
Types of Thermal Paste: Conductive vs. Non-Conductive
There are two main types of thermal paste: conductive and non-conductive. Conductive thermal paste is made from materials that can conduct electricity, such as silver, copper, or aluminum. Non-conductive thermal paste, on the other hand, is made from materials that do not conduct electricity, such as silicone or ceramic.
Conductive Thermal Paste
Conductive thermal paste is typically more effective at dissipating heat than non-conductive thermal paste, as it can transfer heat more efficiently. However, it is also more prone to causing electrical short circuits if it comes into contact with electrical components, as it can allow electricity to pass through it.
This is why conductive thermal paste is generally not recommended for use in electronics, as it can potentially damage the components or even cause a fire.
Non-Conductive Thermal Paste
Non-conductive thermal paste, on the other hand, is much safer to use in electronics as it does not conduct electricity. It is made from materials that can transfer heat effectively but do not allow electricity to pass through them.
This makes it the preferred choice for electronic devices, as it reduces the risk of electrical issues.
Contamination and Electrical Conductivity
It is important to note that even non-conductive thermal paste can become conductive if contaminated with conductive materials, such as dust or metal particles. This can occur if the paste is applied incorrectly or not correctly stored and handled.
In such cases, the paste can cause electrical issues even if it is non-conductive.
Handling and storing it properly is essential to ensure that your thermal paste remains non-conductive. Avoid exposing it to dust or other contaminants, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for applying it to your device.
Is Cooler Master Thermal Paste Conductive?
The Cooler Master Thermal Paste is a high thermal conductivity compound for CPU coolers. Its performance is impressive, boasting 9 W/mK, which allows it to effectively transfer heat from chipsets to cooler bases.
This superior compound can be used across different PC components, making it an excellent choice for advanced overclocking and cooling setups requiring higher thermal efficiency.
Additionally, its formulation allows for low usage without reducing its effectiveness, allowing users to get maximum cooling efficiency out of their preferred budget.
How Can You Protect A CPU From Electrostatic Discharge?
Protecting a CPU from Electrostatic Discharge ensures your computer functions normally. A great way to protect against ESD is to use a grounded Electrostatic Discharge mat or a grounding mat, also known as an antistatic mat.
These mats create an effective barrier between you and the CPU, allowing any static electricity you may introduce into the environment to be dispersed safely.
If you don’t have access to one of these mats, you can reduce the risk of ESD by wearing anti-static clothing and touching items with conductive materials like plastic bags. These measures will help keep everyone – and the hardware – safe!
Will Static Electricity Damage A Computer?
Static electricity is an invisible yet potentially destructive force that can cause widespread damage to computers. Most computer owners are unaware of the risks associated with static electricity as the discharge often happens at voltages too low for humans to feel.
However, when this voltage builds up enough, buying a new device or replacing an entire computer can be the result. This low-level voltage can range in its severity of damage – from a plug-and-play device ceasing to function all the way to completely crashing your whole system.
Always exercise caution and take care of any potential electrostatic discharges near your computer equipment!
Conclusion
Thermal paste conductivity depends on the type of paste in question. Conductive thermal paste is made from materials that conduct electricity, while non-conductive thermal paste is made from materials that do not.
Conductive thermal paste is generally more effective at dissipating heat but is also more prone to causing electrical issues if it comes into contact with electrical components. Non-conductive thermal paste is safer in electronics as it does not conduct electricity and reduces the risk of electrical issues.
However, it is essential to note that even non-conductive thermal paste can become conductive if contaminated with conductive materials.