The error message “ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED” typically pops up when you’re trying to access a website and the site’s name isn’t correctly typed in or is misspelled. This could also happen if you’re trying to open a file on your computer and the file’s location isn’t correct.
Now that you get the ERR NAME NOT RESOLVED error message, Chrome is indicating that it did not find the IP address that matches the website domain name you entered. If this has happened, you will not be able to access the page because your IP address is needed to establish a connection with the web server.
This error can occur when using Chrome on a desktop (Windows, macOS, or Linux), on a mobile device (Android or iOS), or on both platforms. This error is not limited to the Chrome browser. You can also encounter it on other websites, such as Firefox or Safari.
If you’ve ever tried to open a website and gotten an error message that says “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED,” you know how frustrating it can be. Luckily, there are some simple steps you can take to fix the problem. In this blog post, we’ll show you how to troubleshoot and fix ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED.
We’ll also cover some common causes of this error message and offer some tips for preventing it from happening in the future. So, whether you’re a seasoned blogger or just starting out, read on for help with this pesky error!
What Causes The “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” Error?
One of the most frustrating errors you can encounter while browsing the internet is the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error. This error can be caused by a number of different factors, but the most common culprit is a DNS issue. DNS, or Domain Name System, is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses.
If there is a problem with the DNS server, it can prevent your browser from resolving the correct IP address for a website, resulting in the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error. Another possible cause for this error is a problem with your internet connection.
If your connection is unstable or slow, it can prevent your browser from loading a website properly. Finally, this error can also be caused by antivirus software that is blocking access to a particular website.
If you are encountering this error frequently, it is worth checking each of these potential causes to see if you can resolve the issue.
Best Method To Fix ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED Error
Method 1: Restart Your Internet Router
Many of us have come across the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error while trying to access a website. This can be frustrating, especially if you’re not sure what the cause is. In most cases, restarting your router will fix the problem.
Here’s why: when you type in a website address, your computer sends a request to your router. The router then looks up the address and forwards the request to the correct website. If the router is having trouble resolving the address, it will return an error message.
Restarting your router will clear its DNS cache and allow it to resolve the address correctly. So if you’re getting the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error, try restarting your router and see if that fixes the problem.
And to restart your internet router then you need to follow these steps:
- Locate your router’s power cord and plug it into an outlet.
- Press and hold the reset button on your router for 30 seconds.
- Wait for your router to restart, then try accessing the website again.
If restarting your router doesn’t fix the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error, then you need to follow the next method that can be given below.
Related: How to Fix ERR_NAME_RESOLUTION_FAILED on Google Chrome
Method 2: Check If The Website Is Working
It’s frustrating when you try to visit a website and see the dreaded “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” message. This error can be caused by a variety of factors, but the good news is that it is usually quite easy to fix.
First, let’s take a look at what causes this error. One common cause is that the website’s DNS server is not responding. This can happen if the DNS server is down or if there is a problem with your ISP’s connection to the DNS server.
If you’re seeing the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error, the first thing you should do is check to see if the website you’re trying to visit is actually up and running.
You can do this by following these steps:
- To open Windows Terminal or Command Prompt, you need to press the Windows+X button and select it.
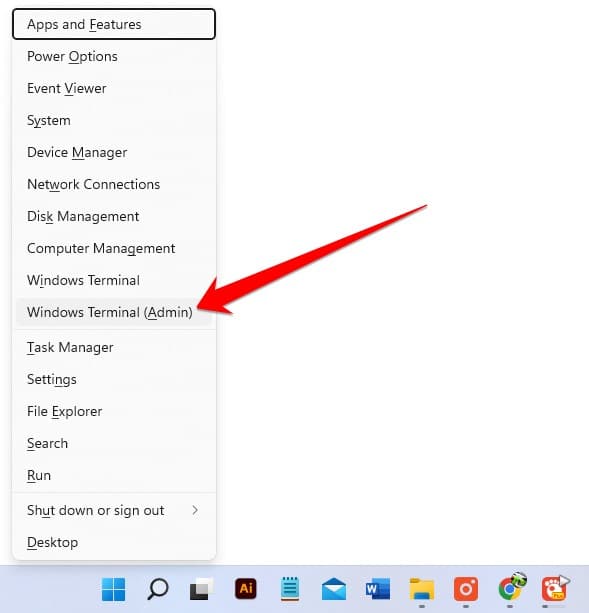
- Now in Windows Terminal, you have to type “nslookup” and then enter the domain of your desired website. So that you know if this website is working properly, or if this website is dead.
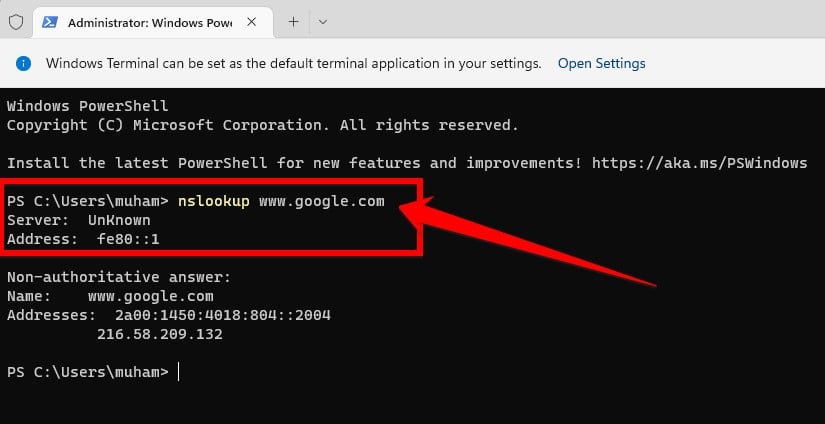
If the invalid attribute is exclusive to connections created with [HTTP/S] requests and it does not return an honest IP address, if it informs that the domain is disconnected, or if there are any other errors, then you may expect to see an issue with your website.
If you’re the webmaster, you ought to check your host until you fix the issue.
While the website proprietor, if you are heading to the website we recommend that you wait and attempt to enter again later so that you can see if the issue is resolved. If you were getting a Valid IP Address and all the website was working fine, you could follow the next method given below to fix the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
Method 3: Change Your DNS Server
Here is another method that can help you to solve this issue in a few simple steps. If you’ve ever seen the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error, it can be pretty frustrating. This error occurs when your computer is unable to communicate with a DNS server, which prevents you from accessing websites.
Here is a simple fix for this error: simply change your DNS server. By doing this you can need to follow the steps given below.
- Open up the Settings app on your computer by pressing the Windows+I button together.
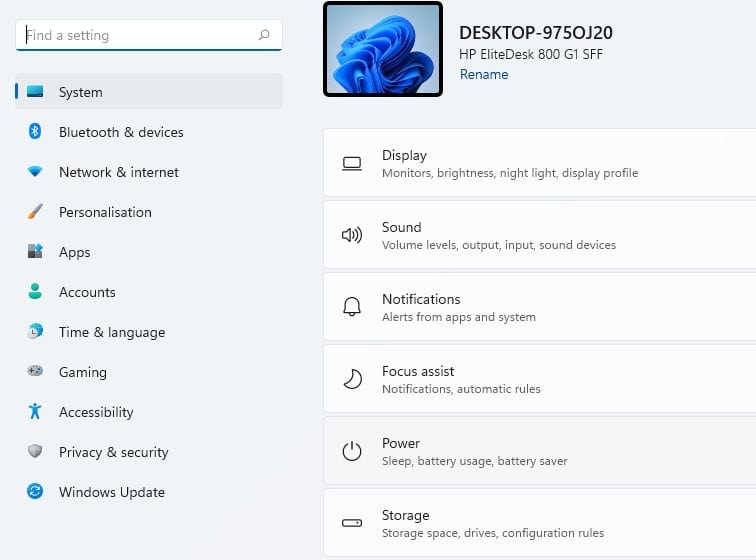
- Once Windows settings have been open, now you need to click on the “Network & Internet” option.
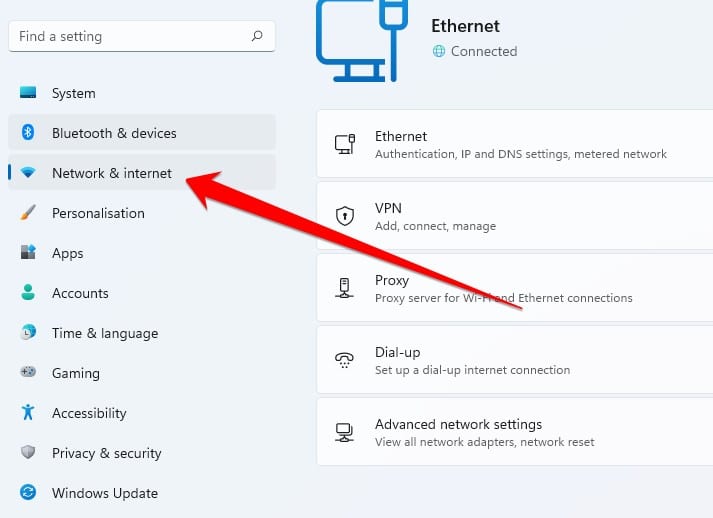
- Here you need to click on the Advance network setting.
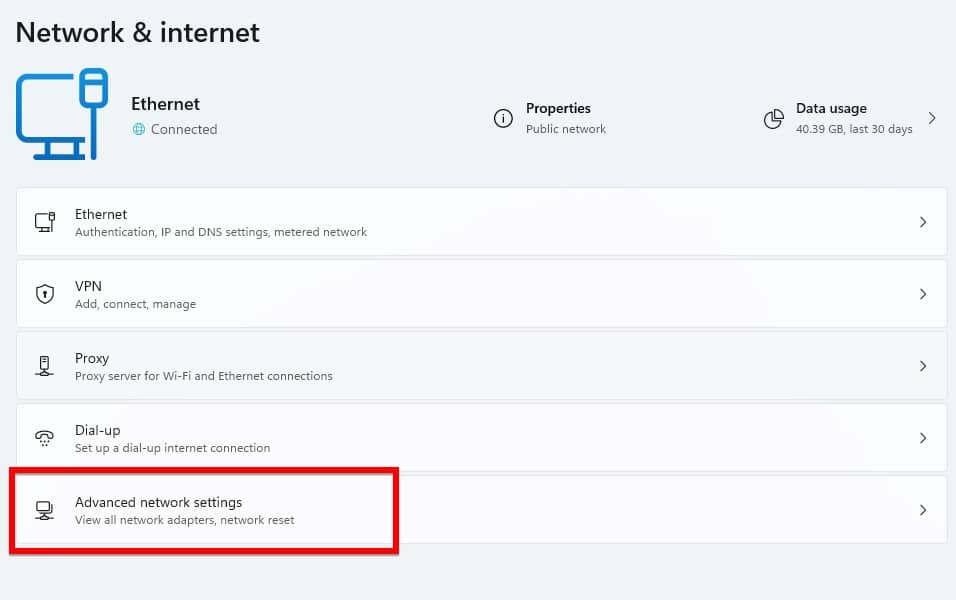
- In Advanced Network Settings, click on “More network adapter options.”
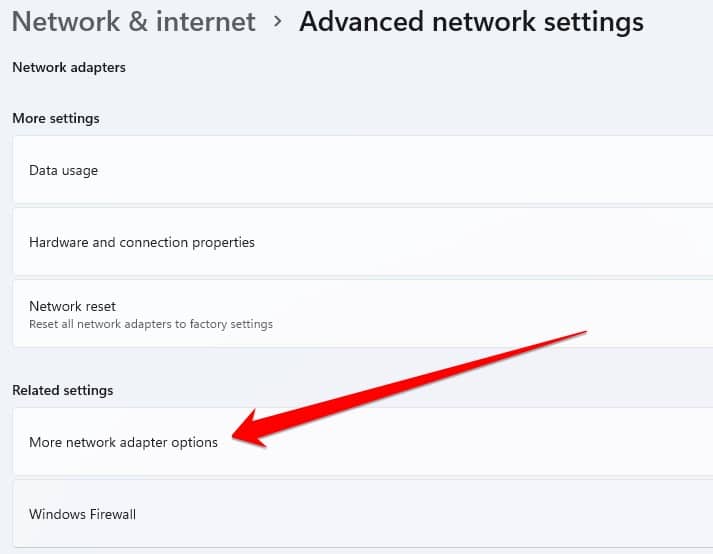
- A new window will open in front of you regarding Network Connection, in which you have to right-click on the icon of Internet connection and go to Properties.
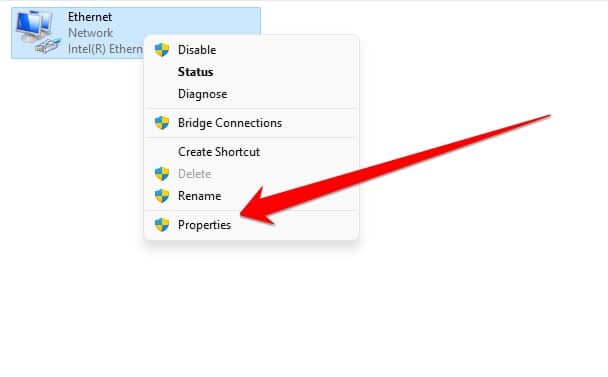
- After visiting the property, you have to double-click on the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)” option.
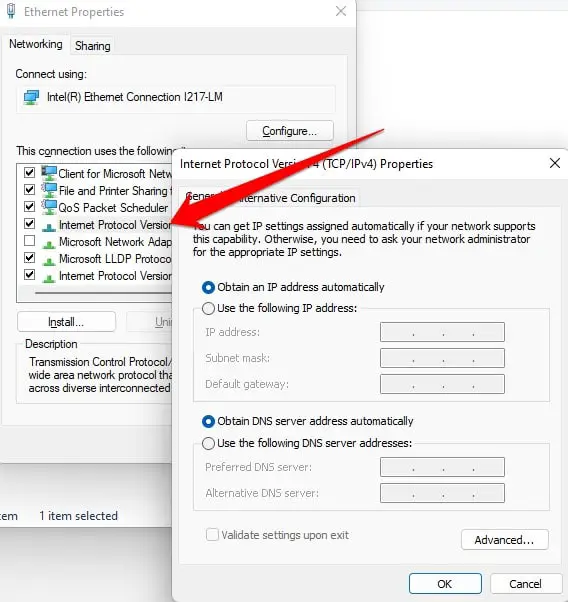
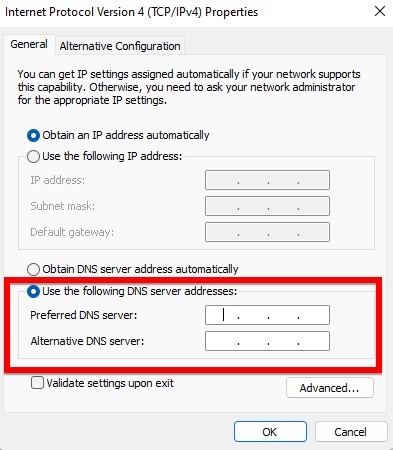
- Select the option “Use the following DNS server addresses”.
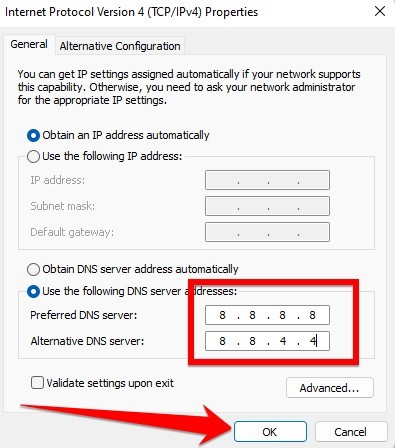
- At the end simply add “8.8.8.8” in the preferred DNS server and “8.8.4.4” in the alternate DNS server, in the given option and save this setting, and press okay to continue.
Method 4: Clear Chrome’s Host Cache
Chrome’s host cache is a hidden feature that speeds up page loading by caching DNS data. However, sometimes the data stored in the cache can become outdated or corrupted, which can lead to errors like ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED. If you’re seeing this error, clearing Chrome’s host cache may help.
Here is the guideline to clear the Google Chrome host cache:
- Type chrome://net-internals/#dns into Chrome’s address bar and press Enter.
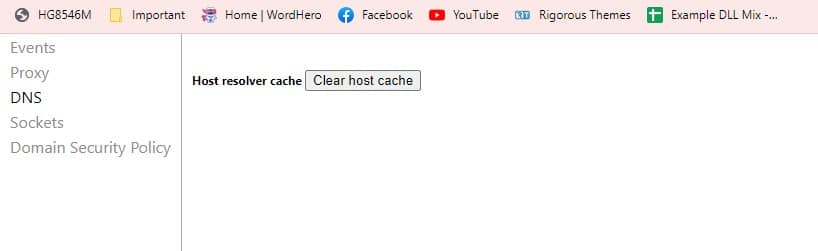
- Click on the Clear host cache button. This will clear all the DNS data stored in Chrome’s host cache.
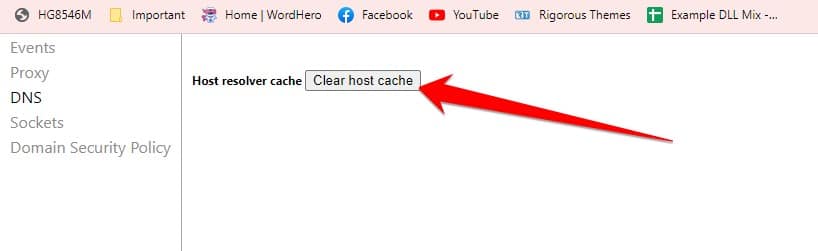
- Close and restart Chrome for the changes to take effect.
- Try loading the desired website page again to see if this issue solves or not.
Method 5: Disable The “Preload Pages” Option
The “Preload Pages” option is a new feature in Google Chrome that aims to speed up your browsing experience by preloading pages that you might navigate to next. However, this feature can sometimes cause the error message “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED”. If you’re seeing this message, disabling the “Preload Pages” option should fix the problem.
Here’s how to do it:
- In your browser URL bar, type chrome://settings/cookies and press Enter.
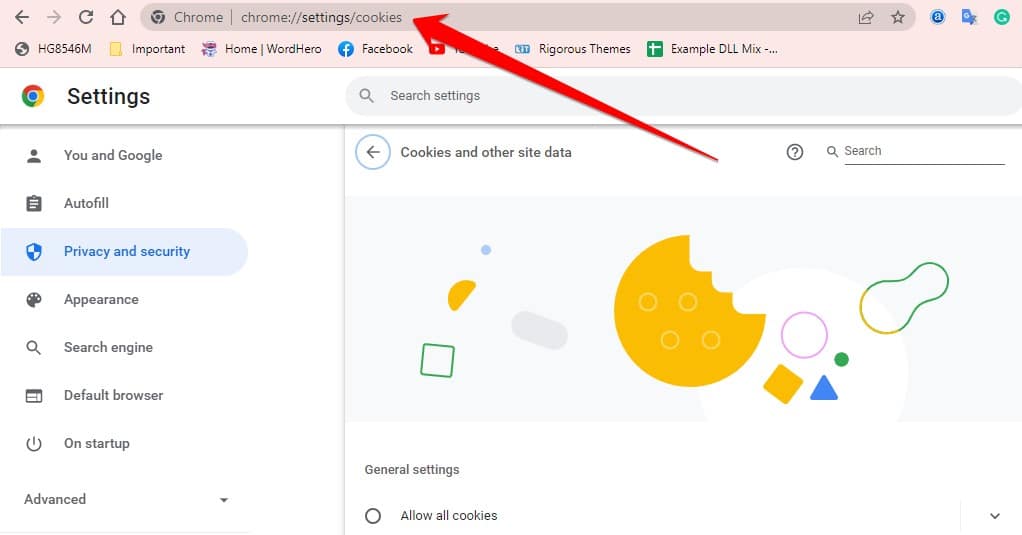
- After coming to this setting page, you should find the “Preload pages for faster browsing and searching” option and make sure that this option is unchecked.
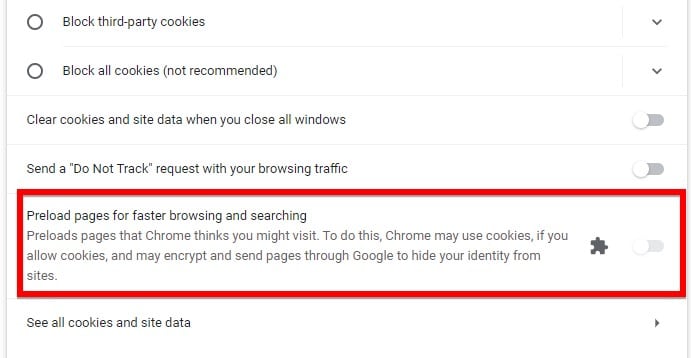
- At the end of this process restart your browser for the changes to take effect.
Once you’ve disabled the “Preload Pages” option, you shouldn’t see any more ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Some Sites Are Not Opening In Google Chrome?
There are a number of reasons why some sites are not opening in Google Chrome. One possibility is that the site is not compatible with the browser. Another possibility is that the site is not properly configured.
Additionally, the site may be experiencing technical difficulties. However, the most likely reason why some sites are not opening in Google Chrome is that the browser has been set to block them.
To fix this problem, follow these steps:
- Go to the “Settings” menu and click on “Show Advanced Settings.”
- Then, under the “Privacy” section, click on “Content Settings.”
- Finally, under the “Cookies” section, make sure that the “Block third-party cookies and site data” checkbox is unchecked.
- By following these steps, you should be able to access any site that was previously blocked by Google Chrome.
How Do I Clear My DNS Cache In Chrome?
If you’re experiencing issues with webpages loading slowly or improperly, it may be due to a problem with your DNS cache. Your DNS cache is a temporary record of all the websites you’ve visited recently, and if it becomes corrupted, it can cause all sorts of problems.
Luckily, clearing your DNS cache is a fairly simple process.
To clear your DNS cache in Chrome, follow these steps:
- Open the browser and type “chrome://net-internals/#dns” into the address bar. This will take you to the DNS page in Chrome’s Settings.
- At the top of the page, you’ll see a button that says “Clear host cache.”
- Go ahead and click that, and your DNS cache will be cleared.
- You may need to restart your browser for the changes to take effect, That’s all there is to it!
Is It Safe To Flush DNS Cache?
There are many benefits to flushing DNS cache, and it’s a perfectly safe process. First, let’s talk about what a DNS cache is. When you visit a website, your computer stores the IP address of that site in its DNS cache.
This helps to speed up the process of loading subsequent pages from that site, as your computer doesn’t have to look up the IP address each time. Flushing the DNS cache simply means clearing out this stored information.
So, here’s no reason not to flush the DNS cache – it’s safe and simple to do, and it can often help to fix minor connection issues. So go ahead and give it a try!
How Often Should You Flush Your DNS Cache?
If your DNS cache gets corrupted, it can lead to all sorts of problems, from webpages not loading properly to email correspondence being disrupted. That’s why it’s important to know how to flush your DNS cache. But how often should you do it? The answer may surprise you.
It turns out that there is no need to flush your DNS cache very often. In fact, unless you are experiencing problems, you can probably get away with flushing your DNS cache once a month or even once every few months.
Of course, if you are having DNS-related issues, then you may need to flush your cache more frequently.
So there you have it: there is no need to flush your DNS cache more than once every few months, unless you are having problems. If you do need to flush your cache more frequently, remember to do it only when absolutely necessary.
Does Flushing DNS Help Ping?
Flushing your DNS cache can help to improve your pings. When you flush your DNS, you are telling your computer to discard any information that it has stored about domains and IP addresses. This allows your computer to query domain names and IP addresses anew, which can sometimes result in better ping times.
However, there are a few things to keep in mind before you flush your DNS. First, flushing your DNS cache may not always result in improved pings. Second, flushing your DNS can cause temporary problems with accessing websites or services.
Finally, some ISPs may block access to their DNS servers if you try to flush them yourself.
Does Flushing DNS Help Packet Loss?
Packet loss is a common problem that can have a variety of causes, from interference to congestion. While there are many ways to try to address packet loss, one option that is often recommended is flushing the DNS cache. But does this actually help?
To answer this question, we first need to understand what DNS is and how it works. DNS stands for Domain Name System and it is essentially a directory of websites that maps domain names (such as google.com) to IP addresses (such as 172.217.22.206).
When you visit a website, your computer contacts a DNS server to get the IP address for that website. This server then sends back the IP address and your computer connects to that address to load the website. One common way of dealing with packet loss is by flushing the DNS cache on your computer.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve ever encountered the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error while trying to access a website, then you know how frustrating it can be. This error can prevent you from being able to access the site in question, and it can also make it difficult to determine the cause of the problem.
As shown above, there are several methods that you can use to fix this error. One common method is to simply restart your computer. This will often clear up any DNS issues that may be causing the problem.
Another method is to clear your browser’s cache and cookies. This can sometimes resolve the issue if it is caused by a corrupt or outdated file. Finally, you can try using a different DNS server. If you are using a public DNS server, such as Google DNS, you can try switching to another public server, such as OpenDNS.
If none of these methods work, then you may need to contact your ISP or the website owner for further assistance.