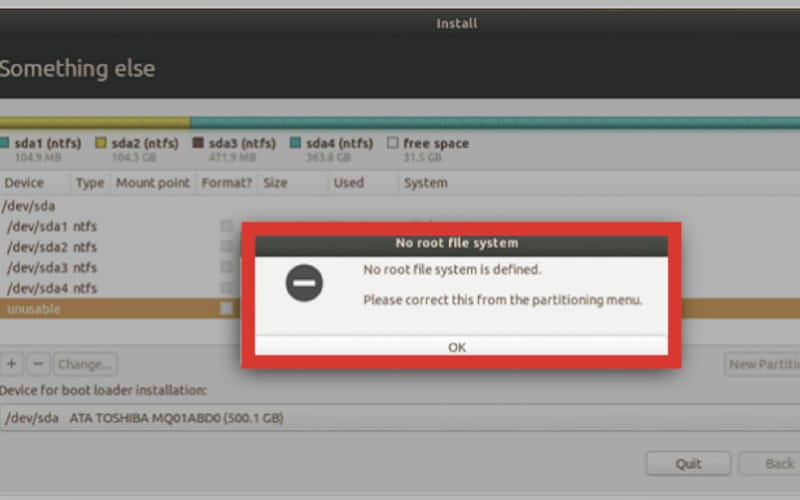
Linux is a versatile and open-source operating system that you can use on your computer, server, or embedded device. One of the most common errors when using Linux is the “No Root File System is Defined” error.
Several factors can cause this error, but most often, it is caused by an incorrect or missing root file system. If you are getting this error, don’t worry. In this article, we will show you how to fix the “No Root File System is Defined” and make your computer run normally and able to access the correct partition.
What Causes “No Root File System Is Defined” Error?
If by any chance you happen to receive the “No Root File System is Defined” error, it means that during the installation process, Ubuntu/Linux could not detect the root partition when it was trying to install the OS.
Partitions are sections of your computer’s hard drive that you can use to keep your data organized. The root partition is where the core files of your Ubuntu/Linux installation are located.

For Ubuntu/Linux to be installed correctly, it needs to be able to find the root partition. If it can’t find the root partition, you will receive the “No Root File System is Defined” error.
Below are the leading causes of this error:
- You are trying to install ubuntu on a FAT/ FAT32 Partition, a windows partition.
- You don’t have a valid created Linux partition.
- You have not defined your root partition.
How To Fix “No Root File System Is Defined”?
When you receive the “No Root File System Is Defined” error message, your computer cannot find the file system’s root directory. It can prevent you from accessing your files and your computer from booting up. There are a few things you can try to fix this problem.
You must follow the outlined solution to restore your computer to working condition:
1. Create The Linux Partition And Assign It As Root
You only need to create a Linux partition and assign it as root to solve the error. This helps when the root directory needs to be assigned correctly.
You can make the partition and set it as root by following the steps below:
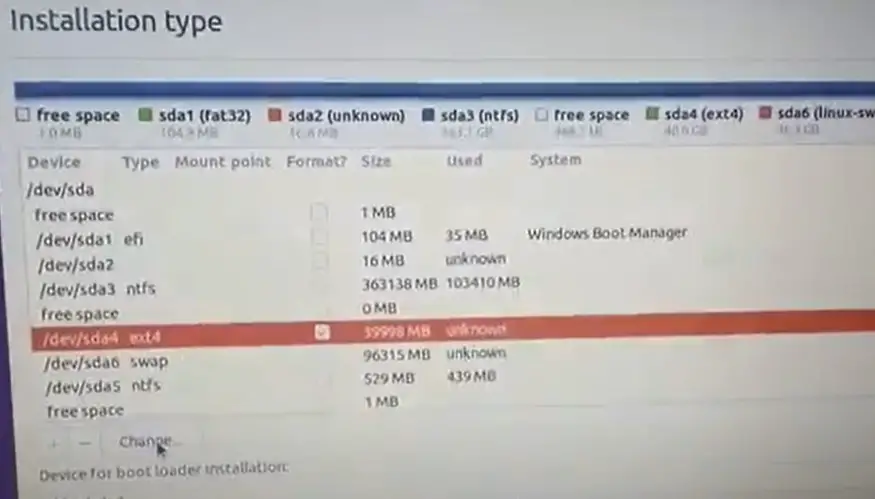
- You need to choose the free partition from the installation page. Add the partition by clicking on the + sign. Now the create partition will be created, which allows you to choose the partition size, type, and location.
- You will need to enter the size of the partition you want to create by filling in the Size field on the partition window. Remember, the size of the partitions should be entered in MBs.
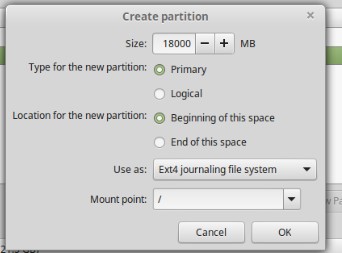
- Select the type of partition. It can be either logical or primary.
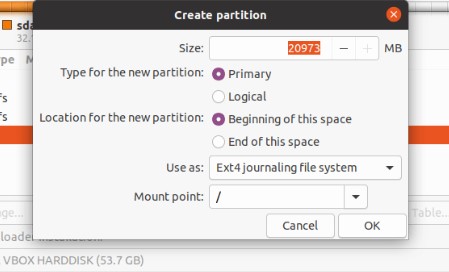
- You can choose between having the new partition at the beginning or end of your allotted space.
- Choose the file system and opt for Mount point. Select the file system you want from the dropdown beside the mount point. Click Ok to finish the process of partition creation.
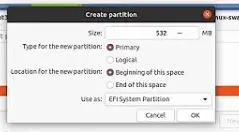
2. Delete Windows Partition That Exists
When you choose a FAT or FAT32 while installing Linux, you will get the error ‘No Root File System is Defined.’ In that case, you need to delete the Windows partition and create a new one. The partition will appear as free after you delete it.
If you need help with how to do that, follow the steps below:
- Go to your partitions and right-click on the one you want to delete (choose the one with your windows). From the options that will appear, click on delete, and your partition will be deleted. You can also choose to Change the partition instead of deleting it. This will allow you to change it to a Linux file system.
- When you click on ‘Change,’ a pop-up with options will appear on your screen.
- Click on Use as dropdown menu and select the file system you want.
- Click on the OK button.
- This will change your Windows partition to root file, and you will not get the error ‘No Root File System is Defined’ again.
3. Define A Root Partition
You can use the fdisk tool to create a new partition on your hard drive and set it as the root filesystem. This helps the computer to find the correct location of the root directory. The no partition should be represented using (/) and as mount in case of /etc/fstab.
You must have free space on your hard drive to create a new partition. Below are the steps you should follow to define the root partition;
- Click on your hard disk space and choose the disk volume you want to change to root.
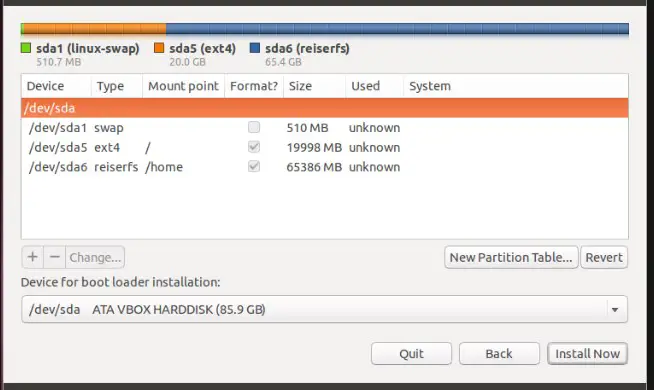
- Right-click on the disk and select change. You can also choose to double-click on the disk.
- The edit option will open, and click on the dropdown next to the mount.
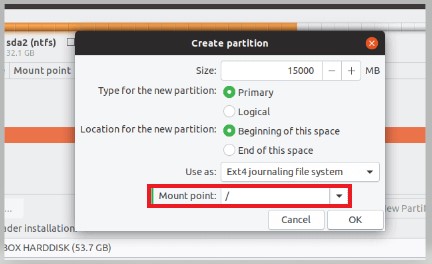
- You will need to select the /. Hit the Ok, and you have successfully set the root partition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Root Partition?
A root partition is a section of a hard drive dedicated to housing the files and data associated with an operating system. The root partition is typically the largest partition on a hard drive and is generally used to store the operating system files. In some cases, the root partition may also be used to store application files.
How Much Is A Root Partition?
A root partition is the main partition on a hard drive where the operating system is installed. The size of a root partition depends on many factors, such as the size of the hard drive, the amount of available space, and the needs of the operating system.
Generally speaking, a larger root partition provides more space for the operating system to install programs and store data. A smaller root partition may be sufficient for a basic installation of the operating system but may need more space for more advanced users.
It is crucial to consider the root partition size when installing a new operating system or to upgrade an existing one. Otherwise, the system may need more space to function correctly.
How Much Space Do I Need For A Root Partition?
The root partition size depends on many factors, such as the hard drive size, the number of installed applications, and the amount of user data. However, a good rule of thumb is to allocate at least 20 GB for the root partition.
You should allocate more space for the root partition if you have a larger hard drive. Remember that the root partition size will also affect the disk space available for other partitions, such as the home partition.
Do I Need A Separate Home Partition?
If you’re new to Linux or want to try it out, you may wonder if you need to create a separate home partition. The short answer is: it depends. Suppose you’re planning on using Linux as your primary operating system or have a lot of data you want to keep separate from your operating system. In that case, creating a separate home partition is a good idea.
Otherwise, you can get away with just using a single partition for your entire system.
There are a few benefits to creating a separate home partition:
- It can make it easier to reinstall your operating system. If you ever need to reinstall Linux, you can format your root partition and leave your home partition intact. This way, you will retain all of your data and settings.
- It can help to keep your data safe in the event of a system crash. If your root partition becomes corrupted, you may recover your data by mounting your home partition on a different system.
- It can make it easier to upgrade your operating system. If you want to upgrade to a new version of Linux, you can install it on your root partition and leave your home partition alone. This way, you will be able to maintain your data and settings.
- It can make it easier to manage your disk space. If you have a lot of data, keep it on a separate partition, so it doesn’t take up too much space on your root partition.
What Is The Root Of The USB?
The root of a USB is the top-level directory of the drive. In other words, it is the starting point from which all other directories and files on the drive are accessed. The root is typically represented by a slash (/), although some systems may use a different character, such as a backslash (\).
The root directory is typically the first location accessed when a USB drive is connected to a computer. From the root, a user can navigate to other directories on the drive. In some cases, the root directory may be hidden from view, and a user may need to type in the full path of a directory to access it.
The root directory can also be used to store files. However, storing files in subdirectories is generally considered good practice, as this can help keep the drive organized.
What Is Root File System In Linux?
The root file system is the file system that contains all the necessary files and directories for the Linux kernel to operate. It is typically mounted on “/” (the root directory). The bootloader usually initializes the root file system (such as GRUB or LILO). Any other file systems are usually mounted on directories under the root file system, such as /home or /usr.
The term “root file system” can also refer to a disk partition that contains the root file system. This is useful for separating the operating system files from user data and can be helpful for recovery in the event of a system crash.
If you are new to Linux, you might wonder what all this talk about the root file system is. The root file system is the most important part of a Linux operating system. It contains all the files and directories for the Linux kernel to operate. The root file system is typically mounted on “/” (the root directory).
How To Create A Root File System In Linux?
You can create a root file system in Linux using various methods. One common method is using a ” dd ” tool to create an image of the root file system. This image can then create a bootable CD or USB drive.
Another method is to use a tool called “mkfs” to create a root file system on a blank hard drive. This method is generally more complicated and is not recommended for beginners.
Once you have created a root file system, you must install a bootloader. This is typically done using the “grub” bootloader. Once the bootloader is installed, you can boot into your new root file system.
If you use a computer with an existing operating system, you may need to modify your bootloader settings to boot into your new root file system. This is typically done by editing the “boot.ini” file.
Once your new root file system is up, you can begin installing software. Most Linux distributions come with a package manager that makes it easy to install the software.
How Do You Create A Root File?
You can create the root file system in several ways. One popular way is to use a tool such as mkfs. Another way is to use a disk partitioning program such as fdisk.
Once you have created the root file system, you need to mount it. The mount point is the location where the file system will be accessible.
What Is The Root Directory In Windows?
The root directory of a drive is the “highest” level directory of that drive. In other words, it is the first or topmost directory in the drive. All other directories on that drive are “subdirectories” of the root directory.
The term “root directory” can also refer to the directory that contains all the files and subdirectories for a particular software program. The Windows root directory is usually something like C:\. In Linux, the root directory is /.
Conclusion
When you encounter the “no root file system is defined” error, your computer cannot find the operating system. This can be caused by various factors, including a corrupt or missing boot sector, a corrupt or missing partition table, or damage to the hard drive’s file system.
The above solutions should help you fix this error and keep your computer running. If you still have difficulty, you may need professional help.