Have you ever heard of CMOS and BIOS? These are two important components of a computer system that many people don’t know much about. I didn’t understand them myself until recently, but now that I do, I can see just how crucial they are to the proper functioning of a computer.
In this article, I will give you an overview of CMOS and BIOS, explain what they do, and discuss their differences. Whether you’re a tech expert or a newbie,
I hope this article will be informative and interesting for you.
What is CMOS?
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a type of chip used to store information in a computer. This chip is responsible for storing important configuration information, such as date and time, hardware settings, and other system information required for your computer to function properly.
One of the reasons why CMOS is so important is because it is non-volatile memory, which means that it can retain data even when the computer is turned off.
This differs from volatile memory, which is lost when the computer is shut down. That’s why CMOS often stores the BIOS settings, which we’ll discuss later.
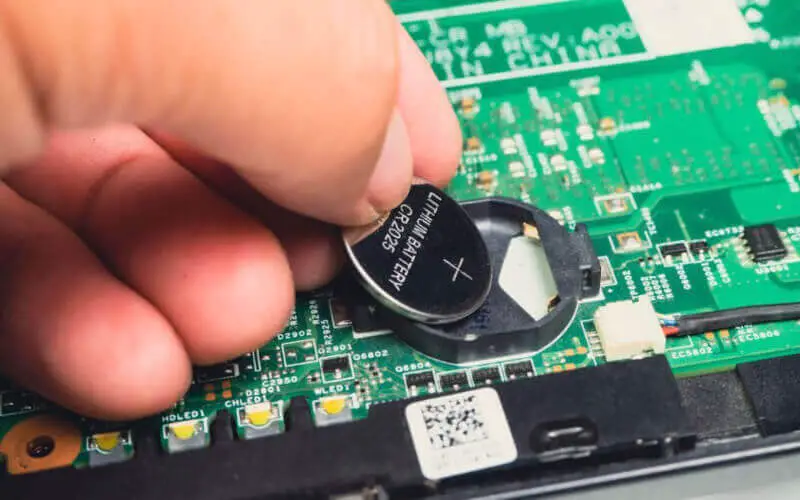
CMOS is typically located on the motherboard of a computer. A small battery powers it to ensure it retains information even when the computer is turned off.
When you turn on your computer, the information stored in CMOS is used by the BIOS to initialize your system and prepare it for booting up.
CMOS is an important computer system component that plays a crucial role in properly functioning your system.
What is BIOS?
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System, software stored on a chip on your computer’s motherboard. BIOS is responsible for initializing and testing your hardware components during the boot process, and it is also responsible for loading the operating system into memory.
When you turn on your computer, BIOS is the first software that runs, and it performs a series of self-tests, known as POST (Power-On Self-Test), to ensure that your hardware components are working properly. If problems are detected during the POST, BIOS will display an error message informing you what went wrong.
Once the POST is complete, BIOS will look for the boot loader for the operating system, which is usually stored on the hard drive. Once the boot loader is found, BIOS will load it into memory and transfer control to the operating system, which then takes over and continues the boot process.
One of the important functions of BIOS is to store the configuration settings for your hardware, such as the boot sequence, which determines the order in which your computer looks for bootable devices and other settings used to configure your hardware components. These settings are stored in the CMOS, which we talked about earlier.
BIOS is an essential computer system component for initializing and testing your hardware components and loading the operating system into memory.
Differences Between CMOS and BIOS
The basic difference between CMOS and BIOS is that CMOS is a type of chip used to store information, while BIOS is a software program stored on a chip.
CMOS stores configuration information, such as date and time, hardware settings, and other system information. At the same time, BIOS is responsible for initializing and testing your hardware components during the boot process and loading the operating system into memory.
Another technical difference between CMOS and BIOS is that CMOS is non-volatile memory, meaning it can retain data even when the computer is turned off. At the same time, BIOS is loaded into memory during the boot process and is volatile, meaning it is lost when the computer is shut down.
CMOS is typically placed on the motherboard of a machine. On the other hand, BIOS can be found on a chip embedded in said motherboard; if needed, one may update or replace the current version with an updated BIOS.
One advantage of CMOS is that it can store important system information even when the computer is turned off, while one disadvantage is that it is limited in terms of storage capacity.
On the other hand, one advantage of BIOS is that it is essential for the boot process and can be updated or replaced with a new version, while one disadvantage is that it can be vulnerable to attacks or malware.
CMOS and BIOS are important components of a computer system that play different but complementary roles in ensuring the proper functioning of your system.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between CMOS and BIOS is important for anyone who wants to understand better how their computer system works.
To understand the foundational roles of CMOS and BIOS, we discovered that CMOS is a chip responsible for keeping essential system configuration details. On the other hand, BIOS serves as a software program to evaluate hardware elements during startup and load up the operating system into memory.
While they have different functions, both CMOS and BIOS are essential components of a computer system that work together to ensure the proper functioning of your system.
So, the next time you turn on your computer, and it goes through the boot process, you’ll better understand what’s happening behind the scenes, thanks to your knowledge of CMOS and BIOS.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does every PC have CMOS?
Every personal computer contains a small battery on its motherboard, known as the CMOS battery, which supplies power to the Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) chip. This chip stores vital system configuration information, including hard disk details, date, and time.
What is the lifespan of a CMOS battery?
The typical lifespan of a CMOS battery is around 3 to 5 years. However, this battery life can be extended to ten years or even more with proper usage.